Most Effective Chest Exercises for Men
Table of Contents
Building a strong chest isn’t just about looking good; it’s also crucial for overall upper body strength. There are countless exercises to target your chest muscles, but some stand out more than others. Here, we’ve compiled a list of the most effective chest exercises for men to help you achieve your fitness goals.
1. Understanding the Anatomy of Chest
1.1 Major Muscles Involved
- Pectoralis Major: Structure and Function: The pectoralis major is the most prominent muscle in the chest, characterized by its large, fan-shaped structure. It plays a crucial role in arm adduction, flexion, and internal rotation, making it essential for many upper-body movements.
- Pectoralis Minor: Role in Chest Development: Nestled beneath the pectoralis major, the pectoralis minor aids in stabilizing the scapula. While it is smaller in size, developing this muscle contributes to a balanced chest structure and proper shoulder mechanics.
- Important Supporting Muscles: In addition to the main pectoral muscles, several supporting muscles, including the deltoids, triceps, and serratus anterior, also assist in chest exercises; their development is vital for overall upper-body strength.
1.2 Importance of a Strong Chest
- Role in Overall Fitness: A strong chest supports essential movements in both daily tasks and sports. It enhances posture, decreases the risk of injuries, and aids in the performance of various physical activities.
- Impact on Athletic Performance: Many athletic skills, from throwing to pushing, rely heavily on chest strength. A well-developed chest can lead to improved performance in sports like football, basketball, and weightlifting.
- Contribution to Aesthetic Goals: For many, a well-defined chest contributes to an attractive physique. A strong chest is often associated with masculinity and fitness, making it a common goal among men.
1.3 Factors Affecting Chest Muscle Growth
- Genetics and Muscle Fiber Types: Some individuals are predisposed to greater muscle growth, primarily due to genetics that determine muscle fiber types. Fast-twitch fibers, for example, are generally more responsive to hypertrophy.
- Nutrition and Recovery: Proper nutrition, including adequate protein intake, is critical for muscle repair and growth. Recovery periods also play a pivotal role in allowing muscles to rebuild stronger after workouts.
- Training Frequency and Intensity: Consistency in training, combined with varied intensity levels, is essential for promoting muscle growth. Incorporating progressive overload into your routine can help in continuous strength gains.
2. Bench Press Variations

The bench press is a staple in any chest workout routine. It’s one of the best exercises for building mid-chest strength and size. This exercise allows you to lift heavy weights, making it ideal for muscle growth.
2.1 Flat Bench Press
- Proper Form and Technique: Start by lying flat on a bench, feet on the ground, and grasp the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width. Lower it to your chest and push upwards, ensuring your elbows remain tucked in to avoid shoulder strain.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid: Avoid arching your back excessively and ensure that your wrists are straight. Do not bounce the bar off your chest, as this can lead to injury.
- Benefits for Overall Chest Development: This classic exercise targets the entire pectoral region, promoting balanced development and strength.
2.2 Incline Bench Press
- Targeting the Upper Chest: The incline bench press shifts focus to the upper part of the pectoral muscles, essential for well-rounded chest aesthetics.
- Equipment Options and Variations: You can use a barbell or dumbbell for this exercise. Some gyms also offer adjustable benches for added versatility.
- Recommendations for Beginners: Start with lighter weights to master the form before progressing to heavier loads.
2.3 Decline Bench Press
- Focusing on the Lower Chest: This variation allows for greater emphasis on the lower pectoral muscles, helping to create depth.
- Adjustments for Greater Resistance: Use a decline bench and keep your feet secured. Consider incorporating chains or bands for added resistance.
- Safety Tips and Alternatives: Ensure a spotter is present, particularly with heavier weights. Alternatives include dumbbell decline presses.
3. Bodyweight Chest Exercises

3.1 Push-Ups
- Variations for Different Fitness Levels: Standard push-ups can be modified with knee push-ups for beginners or explosive push-ups for advanced practitioners.
- Proper Hand Placement and Form: Hands should be positioned shoulder-width apart, with a straight body line from head to heels during the movement.
- Benefits Beyond the Chest: Push-ups engage the core, shoulders, and triceps, making them a comprehensive upper-body exercise.
3.2 Dips
- Targeting the Chest vs. Triceps: While dips mainly target the triceps, leaning forward during the exercise emphasizes the chest.
- Body Positioning for Proper Engagement: When performing dips, keep your torso slightly angled forward to maximize chest engagement.
- Variations for Increased Difficulty: Adding weight with a belt or performing Korean dips can enhance the challenge.
3.3 Plyometric Push-Ups
- Developing Explosive Strength: These dynamic push-ups elevate you off the ground, developing power in the chest and arms.
- Safety Considerations and Technique: Start with a solid push-up form and ensure your landing is controlled to avoid injuries.
- Progressions for Enhanced Performance: Begin with clapping push-ups and progress to more complex variations as strength improves.
4. Free Weights for Chest Training
4.1 Dumbbell Bench Press
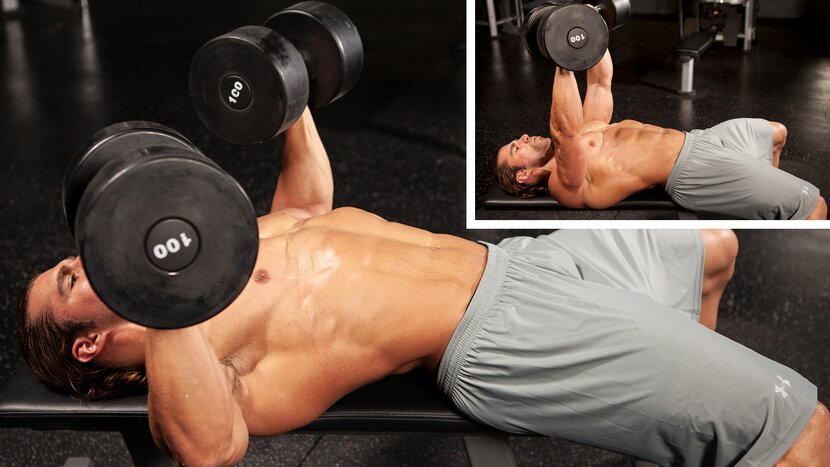

- Advantages Over Barbell Press: Dumbbells allow for a greater range of motion and can help in addressing strength imbalances.
- Essential Techniques for Safety: Keep your elbows at a 45-degree angle to your body and position your feet flat on the ground.
- Incorporating Different Angles: To engage various muscle fibers, perform this exercise on a flat, incline, and decline bench.
4.2 Dumbbell Flyes

Dumbbell flyes are a fantastic single-joint exercise for the chest. Unlike multi-joint exercises like the bench press, which involve both the shoulder and elbow joints, dumbbell flyes focus mainly on the shoulder joint. This makes them excellent for isolating the pectoralis major muscles.
- Targeting the Chest from Different Angles: This exercise isolates the chest muscles and allows for extensive stretching and contraction.
- Importance of Control and Range of Motion: Maintain a slow and controlled movement to prevent injuries and maximize effectiveness.
- Common Errors and Corrections: Avoid bending your elbows excessively, and ensure you do not go too low, which could strain the shoulders.
4.3 Kettlebell Press
- Unique Benefits of Kettlebell Training: Kettlebells add instability to the press, improving core stability and muscle engagement.
- Proper Grip and Form: Hold the kettlebell with a neutral grip. Keep your wrist straight and press directly overhead.
- Incorporating into a Comprehensive Routine: Include kettlebell exercises alongside traditional lifts for a varied approach to training.
5. Cable and Machine Exercises
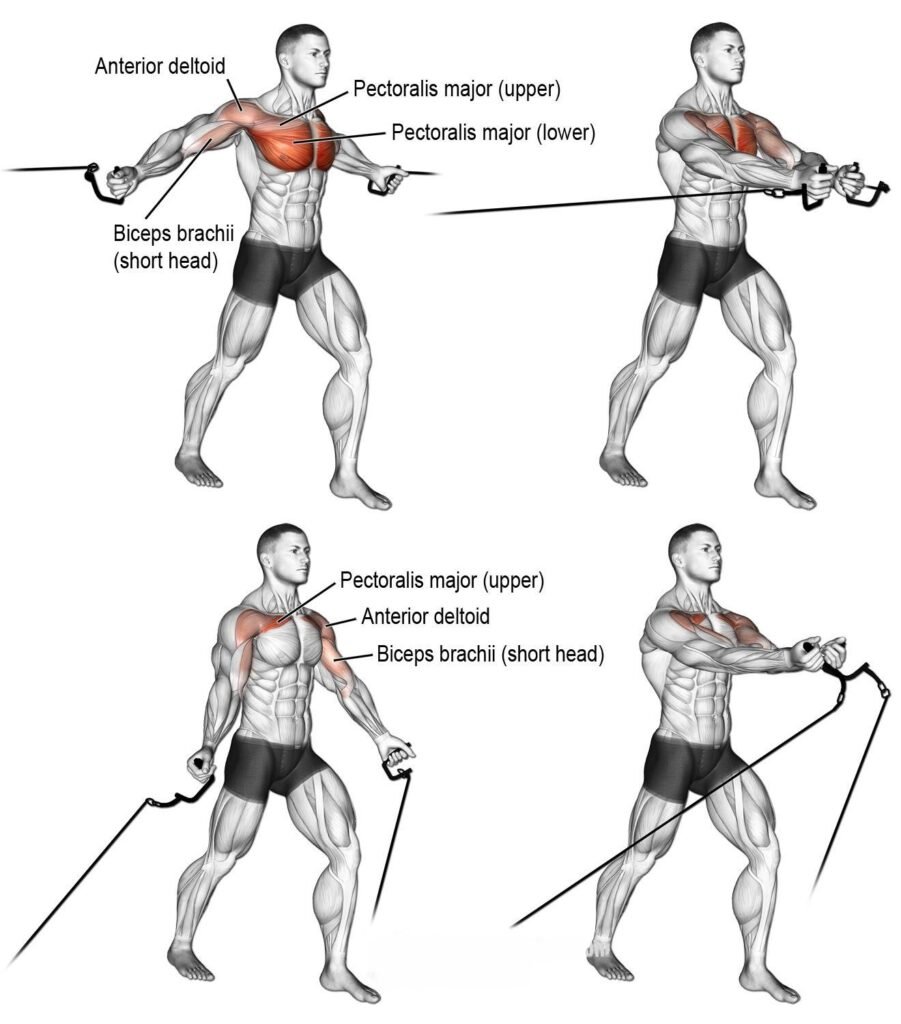
The cable crossover is a fantastic exercise for targeting the chest muscles. It primarily works the chest muscles, including the upper, middle, and lower parts, depending on the height of the handles. This exercise is similar to cable flyes but with a greater range of motion, allowing the hands to cross over each other.
5.1 Cable Crossovers
- Effective Targeting of the Pectorals: Cable machines offer adjustable height features for optimal targeting of both the upper and lower chest.
- Adjusting Cable Height for Variations: Changing cable heights can significantly alter muscle emphasis, allowing for a comprehensive workout.
- Tips for Maintaining Tension Throughout: Focus on controlled movements and continuous tension to engage the muscles effectively.
5.2 Chest Press Machine
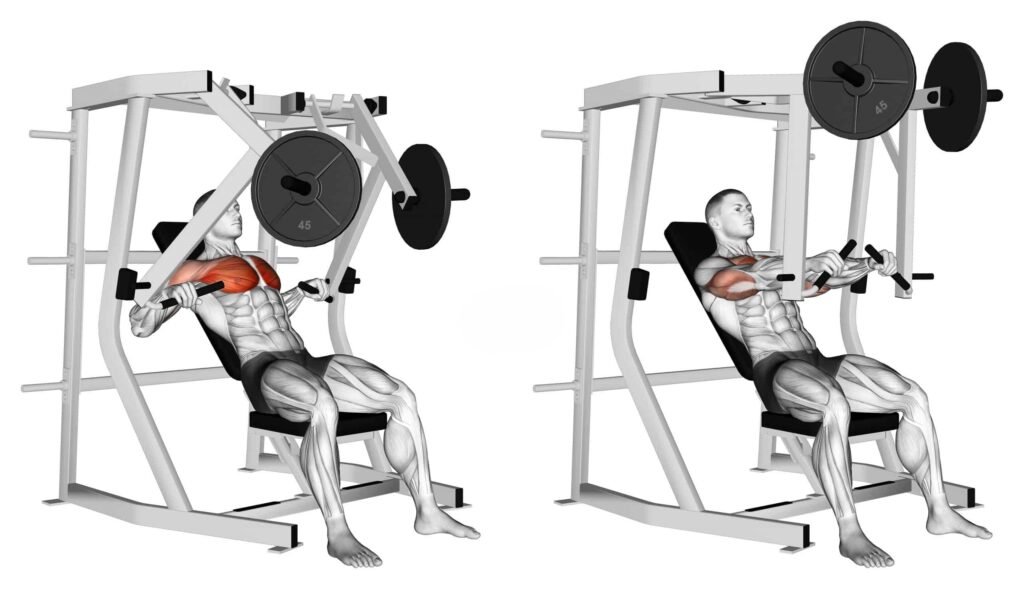
- Benefits of Using Machines for Chest Workouts: Machines can provide guided support, reducing the risk of injury and allowing beginners to focus on form.
- Tips for Proper Setup: Adjust the seat height to ensure proper alignment of the handles with your chest.
- Comparing Machine vs. Free Weight Workouts: Machines may offer stability, whereas free weights promote greater muscle engagement and coordination.
5.3 Pec Deck Machine
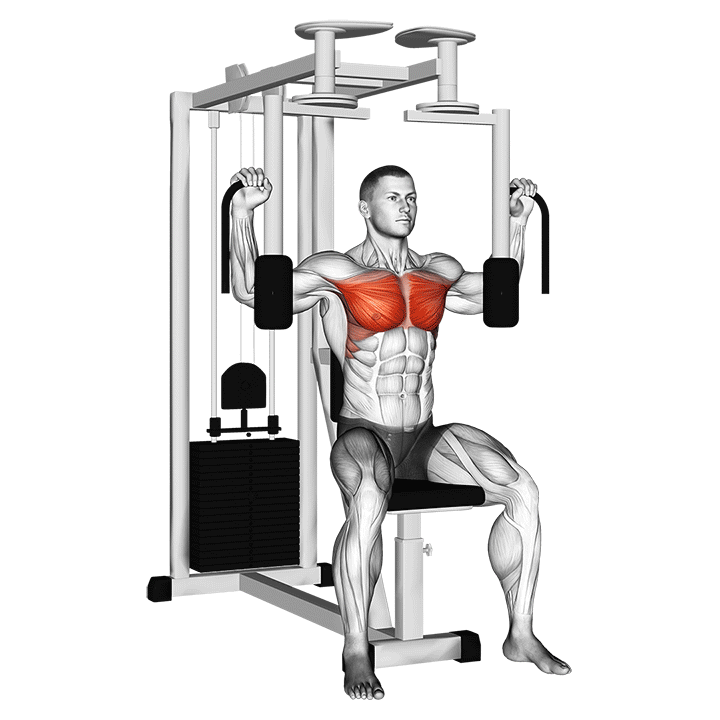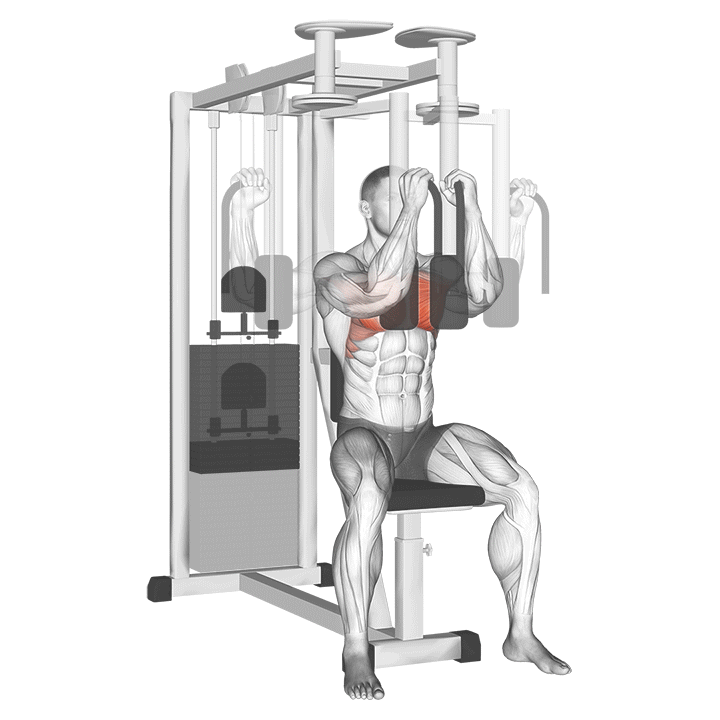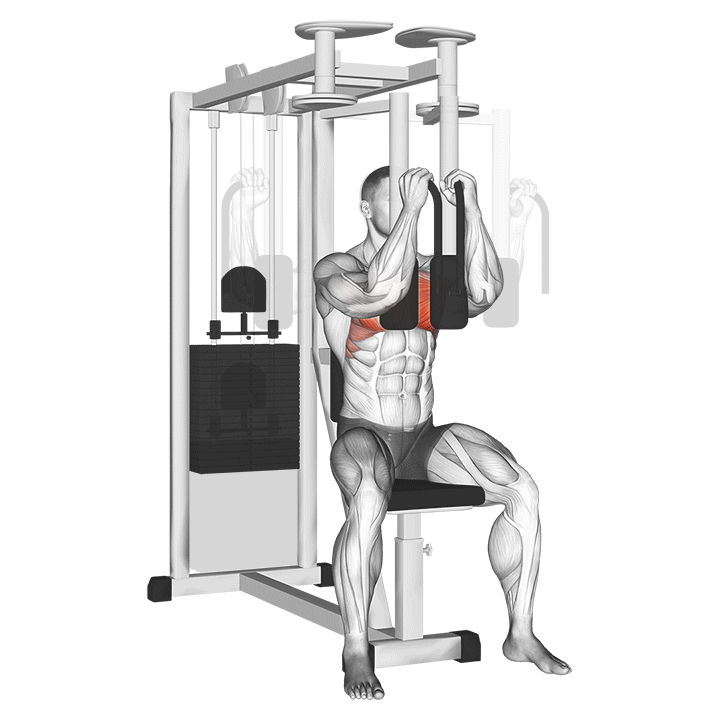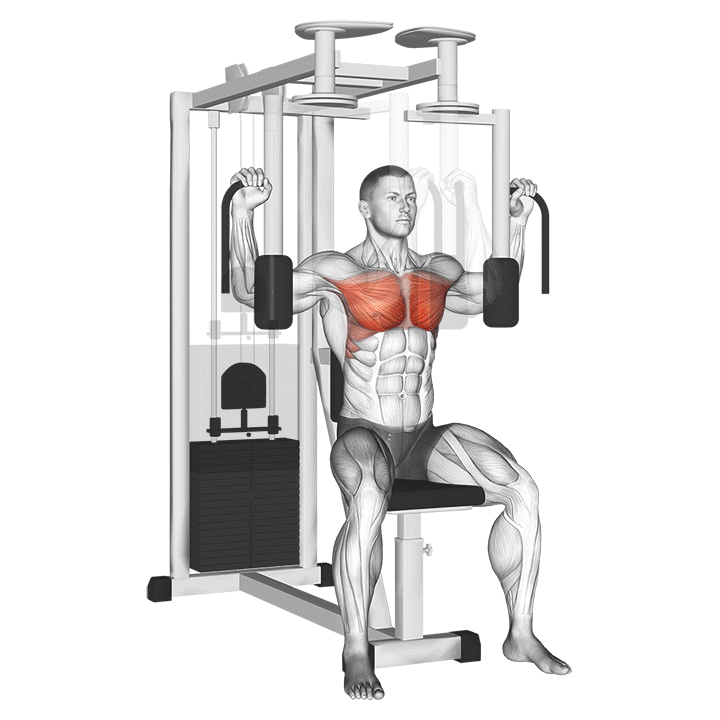
- Isolation of the Chest Muscles: This machine ensures isolation of the pectoral muscles, allowing for focused work.
- Proper Form and Common Mistakes: Sit with your back flat against the pad, and avoid leaning too far forward or back during the movement.
- When to Incorporate into Your Routine: Consider using the pec deck at the end of your workout for a concentrated chest pump.
Summary
- Recap of the 10 Effective Chest Exercises: Incorporating a mix of bench press variations, bodyweight exercises, free weights, and machine workouts can create a robust chest training routine.
- Importance of a Balanced Chest Workout Routine: A well-rounded approach ensures all aspects of chest development are addressed, leading to overall strength and aesthetic goals.
- Encouragement for Consistency and Progressive Overload: To achieve the best results, focus on consistency and gradually increase the weights and intensity of your workouts.
FAQs
- What is the best chest exercise for beginners? Push-ups are an excellent starting point as they require no equipment and can be modified for various fitness levels.
- How often should I train my chest? Training the chest 1-2 times per week allows for adequate recovery while promoting muscle growth.
- Can I build muscle without equipment? Yes, bodyweight exercises like push-ups and dips can effectively build chest muscle.
- What is the role of nutrition in chest development? Nutrition supports muscle recovery and growth; adequate protein intake is crucial for optimal results.
- How do I prevent injury while working on my chest? Always focus on proper form, warm up adequately, and listen to your body to avoid overtraining.

